Have you noticed more and more people walking around your town or city staring at their smartphones and acting a little…weird? If so, there’s no need to panic. These people are most likely playing Pokémon Go, a free augmented reality game for iOS and Android users.
The app harnesses a phone’s GPS to inform players of a Pokémon’s location and uses the device’s camera to combine characters from the game with scenes from the real world. For instance, players may spot a Pokémon on the sidewalk in front of them or outside of their local Starbucks.
The game has undoubtedly proven that augmented reality (AR) is a super fun distraction from the tedium of real life. Just look at the number of people playing it. According to the site TechCrunch, Pokémon Go has more daily users than Twitter and has topped Facebook in terms of engagement.
But beyond being a fun distraction, augmented reality is steadily changing the healthcare landscape and proving it has more serious applications in medtech.
What’s the Difference Between Augmented and Virtual Reality?
Augmented reality and virtual reality (VR) are like cousins: related but quite different. In VR, a 3D world is created that seems incredibly real, however, this world is completely detached from the user’s actual reality. AR, on the other hand, blends a user’s reality with a simulated world. Using AR, a user never loses touch with his or her own reality and yet information can be placed into their view to create an experience. Augmented reality in healthcare is one such application where AR can enhance real-world environments with useful medical information and tools.
Technically speaking, AR is already primed to be used widely across the healthcare industry. The biggest obstacles will be in educating and simply getting providers to adopt the technology.
More Information: AI, virtual reality set to boost the growth of integrated operating rooms
Some doctors have already embraced the AR. Dr. Selene Parekh is an orthopedic surgeon at Duke Medical Center who has been using Google Glass, the wearable computer with a built-in camera and monitor, in the operating room. He uses the glasses to record all of his surgeries and stream live feeds to hospitals in India for training purposes.
Dr. Parekh will no doubt be joined by his peers as more and more healthcare providers adopt AR over the next 3 – 5 years.
Examples of Augmented Reality in Medicine
Let’s take a look at some of the ways this technology will, and already has, impacted the healthcare industry.
Defibrillator Locator
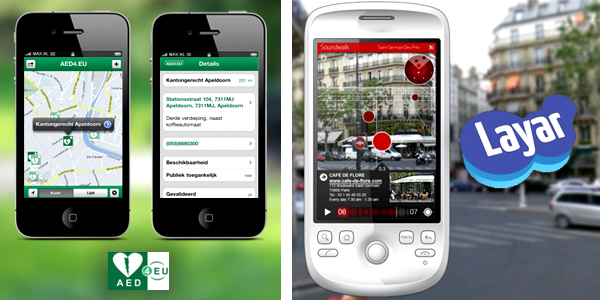
None of us ever want to be in the situation when a stranger next to us suddenly collapses from a heart attack. Besides calling 911 and asking if a doctor is nearby, what do you do?
You can now download the Layar reality browser and AED4EU app to your smartphone, so if you are ever in this situation, you can do more to help. AED4EU was developed in the Netherlands and helps users find automated external defibrillators or AEDs located in their environment. The layer browser projects the exact location of the nearest AED on your phone’s screen so you can locate it easily.
AR in the OR
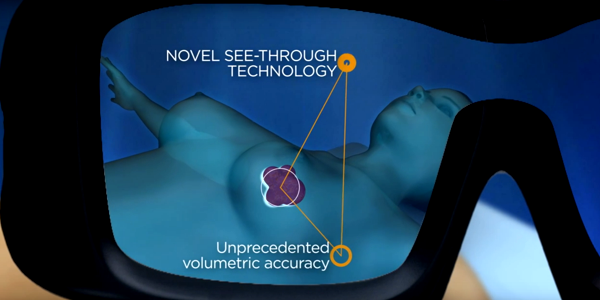
We’ve already learned of one doctor using AR in the OR, but the implication of the technology in this setting are vast. For instance, a company called Medsight Tech have developed a software to test the feasibility of using augmented reality to create accurate 3-dimensional reconstructions of tumors. This technology will essentially give surgeons X-ray vision in real time without the need for any radiation exposure.
Pharma Companies Can Provide More Comprehensive Drug Information
When patients are prescribed drugs, they take them because they trust their doctor, despite any confusion they may have. But most people have no idea how that drug actually works in their body. And attempting to read the pamphlet often increases the confusion.
But AR will change that. With this technology, patients will be able to see how the drug works in 3D animation. And, AR could help lab workers monitor their drug experiments more effectively.
Patients Can Get Tech Help in Describing Symptoms
Most patients struggle to accurately describe their physical symptoms to their doctor. This poses challenges and risks when it comes time to diagnose and come up with a treatment plan.
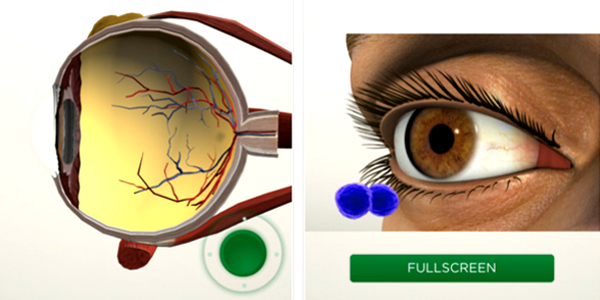
EyeDecide is a medical app that uses the camera display for simulating the impact of specific conditions on a person’s vision. Using this app, an eye doctor can show a simulation of a vision problem. For instance, the app can demonstrate what vision is like for someone with cataracts.
This technology can not only assist in diagnosing conditions, but also help people understand how their lifestyle choices may impact their health in the future, bringing about positive changes.
AR Helps Nurses Find Veins Easier
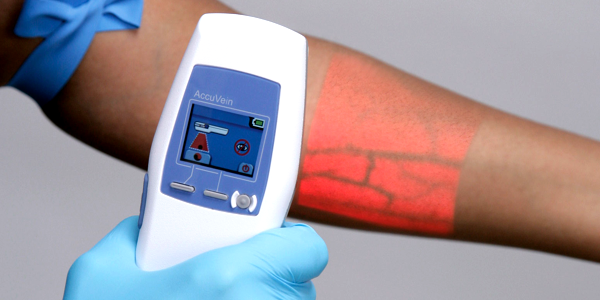
The start-up company AccuVein is using AR technology to make both nurses’ and patients’ lives easier (and a little less painful). The company’s marketing specialist said that 40% of IVs miss the vein on the first stick. Those numbers tend to go up with children and the elderly.
AccuVein leverages AR by using a handheld scanner that projects over skin and shows nurses and doctors where veins are in the patients’ bodies. The technology has already helped more than 10 million patients. This kind of AR technology is incredibly beneficial in helping healthcare professionals advance their skills.
These are just some of the ways AR technology is already positively impacting the healthcare industry. It will be fascinating to see how AR will change the industry for the better in the coming years.